Automatic Transmission Cooling System
In the process of the car movement, the automatic transmission is subjected to significant loads and requires a proper and high-quality cooling. In this article we will consider the automatic transmission cooling system design and its operation principles.
In automatic transmissions, equipped with standard torque converters, coolers are intended to eliminate excessive heat from ATF. ATF is a working fluid which facilitates the torque transmission by means of fluid friction, therefore ATF heats up significantly during operation. Automatic transmissions use the principle of hydraulics and operate with special hydraulic lubricating fluids. Movable parts and numerous gears inside the transmission are in constant movement that invariably leads to the temperature increase.
In CVTs it operates a little bit differently –
here the torque is transmitted using a special belt (or chain) and the
temperature is rising, but not to
such a high level as in automatic transmissions. Today, CVTs are often equipped
with the torque converter, i.e. now CVTs are not rigidly connected with the
engine. On the one hand, it helps to prolong the service life of CVTs, because
there are no hard jerks and kicks from the engine (they are smoothened), but on
the other hand, the temperature inside the CVT is still growing. In any case, it
is required to install a standard cooling system (but it is not always enough).
Normal operating
temperature
A question commonly asked is: what operation temperature is considered to be normal? It is a fair question to ask, but the thing is that there are many different automatic transmissions and they have different operating temperatures. But generally, it is possible to specify the operation range for most of automatic transmissions.
The operating temperature range lies between 65
°C (149 °F) and 95 °C (203 °F). This range of temperatures is considered to be
normal for operation of many automatic transmissions. If the temperature
exceeds 100 °C (212 °F), and even reaches 110 (230 °F)-115 (239 °F) degrees,
then it is necessary to pay close attention to this issue and consult
transmission specialists. Without coolers automatic transmissions will be
unable to deal with high temperatures and consequently it will lead to the
transmission damage.
What does the
automatic transmission cooling system consist of?
The forced cooling system in automatic
transmissions consists of a special pump which builds up the pressure in the
system and pumps the hydraulic fluid from movable parts of the gearbox to a
special oil receiver. This oil receiver is located in the automatic
transmission pan or in the car, thereby allowing efficient cooling of ATF. ATF
is cleaned with the help of a filter, consisting of fine-meshed metal lath or
synthetic material. In the process of operation, ATF loses its properties, therefore
it is necessary to change ATF every 50-60 thousand kilometers. It is also
recommended to replace the transmission fluid filter elements every 25 thousand
kilometers.
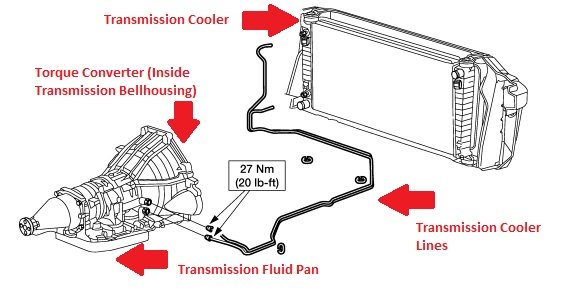
Oil Cooler
The design of the oil cooler for transmission
fluid may vary depending on the specific model of the automatic transmission.
In most models, the oil cooler is located in the engine cooler housing. This
type of the cooling system structure of the gearbox makes it possible to
significantly improve the cooling efficiency of the transmission. Some
transmissions are equipped with enlarged oil coolers, which are necessary for
servicing automatic transmissions with an increased number of gears. Such
transmissions are mainly intended for powerful diesel cars with higher torque.

Automatic Transmission
oil cooler
Car owners must closely monitor technical
conditions of the transmission cooling system. Contamination of the oil cooler
may lead to significant deterioration in ATF cooling efficiency, while presence
of contaminants inside the oil cooler will lead to drop in pressure inside the cooling
system. That is why it is recommended not only to regularly change ATF in the
transmission, but also to perform mechanical cleaning of the cooling system,
because this element often gets clogged with dirt and dust, leading to reduced
cooling efficiency.
Check of transmission cooling hoses

Cooling hose
It'd be a good idea to check the state of transmission cooling hoses in the course of servicing. In the process of the car operation, such hoses may lose their elasticity and be covered with a layer of varnish. It is recommended to replace automatic transmission cooling hoses when the car mileage reaches 100-150 thousand kilometers. It will help to prevent ATF leakages, which can occur in cases of airtightness failures in the cooling system line.
Oil cooler clogging
The oil cooler clogging may lead to issues with
the torque converter. These issues are manifested in problems with the gear
shifting. In addition, there may be partial or complete blocking of the torque
converter operation. In this case, the automatic control mechanism will cut off
the engine when gears are switched. Wear products accumulate in ATF during the
operation of the automatic transmission that, in turn, can lead to the cooling
line valve wedging. In this case, the risk of the automatic transmission
failure due to overheating increases. That is why it is necessary to monitor
the valve state and quality of ATF.
How to clean the oil cooler?
The process of the oil cooler cleaning and ATF
change is quite simple. With proper experience and special equipment, it is
possible to perform the oil cooler cleaning independently. First of all, it is
required to disconnect the line from the transmission cooling system. The
cooling tube of the automatic transmission can be disconnected only when the
car is not running. The cleaning equipment hoses are connected to the radiator
hoses. Active liquid flows through the cooling oil cooler under high pressure with
the help of a special device, allowing to wash out wear products, slag
deposits, bunches of old oil.
After that, it is required to switch off the
cleaning device and connect an air compressor to oil cooler hoses. Under high
pressure, the oil cooler gets dry. Then it is necessary to connect the oil
cooler to the automatic transmission cooling system.
Harmful effects of
overheating
Now we will consider harmful effects of ATF
overheating using the example of the automatic transmission:
- First of all, overheating has a negative impact on ATF itself (ATF threshold amounts to 120 -130 °C (248-266°F). The automatic transmission may heat up to critical temperatures (120-130 °C (248-266°F)) in traffic jams (especially in summer) or in case of aggressive driving. In such situations ATF starts losing its properties that is harmful for numerous units of the automatic transmission.

- Friction discs. Automatic transmissions comprise of numerous soft and hard parts. Soft elements of the automatic transmission rapidly lose their qualities and get damaged under high temperatures (above 100 °C (212 °F)). Therefore, friction discs must be cooled.

- Valve body and solenoids. Nowadays solenoids are often made with addition of plastic, therefore high temperatures are extremely harmful for these components. In addition, there are cases when valve bodies also get overheated.

- Wiring. The automatic transmission wiring also can burn when exposed to high temperatures.
It is hardly a complete list of possible issues
caused by overheating. Lack of proper transmission parts lubrication may lead
up to the damage of planet gears. Therefore, the transmission fluid radiator is
a must for cars equipped with automatic transmissions.
Old automatic transmissions and a separate cooler

In many cases, old automatic transmissions are equipped with a separate transmission cooler, which is installed next to the main cooler. It is considered to be a right solution. In old transmissions the cooler was separated from the engine and was blown over by air or radiator cooling fan, which excluded any chance of overheating (under the condition that ATF is change properly and timely). Therefore, old automatic transmissions were very reliable and their mileages frequently reached hundreds of thousands of kilometers.
Transmission cooler
built in the main radiator
It is considered to be a new milestone in the
automatic transmission cooling. The thing is that in some cars the engine radiator
also includes a special tube, which cools ATF. In other words, the main cooler
is somewhat divided into two parts – one part is responsible for the engine
oil, while the other one prevents the automatic transmission overheating. These
two parts are separated by a special baffle, which does not allow mixing of the
engine oil and ATF.

It seems like a simple and efficient design
solution (two-in-one), but there are several important points to be taken into
account:
- There are so-called high-temperature engines, which can operate at 100-110 °C (212-230 °F), while for automatic transmissions such temperatures may be damaging.
- The size of the abovementioned tube (or its part), located in the cooler, is quite small, therefore the cooling efficiency is not high and overheating is still possible.
Built-in coolers are less efficient than
separate coolers. However, such solution may be enough for new cars. But over
time, dirt will start accumulating on sides of the radiator hoses as well as on
the automatic transmission itself. Even if you change ATF, replace the filter,
but do not clean the system (in particular the radiator), then the cooling
efficiency will deteriorate. The transmission will heat up to 100 °C (212°F) or
even higher. The wear rate of automatic transmission components will increase
significantly. What should be done? Read on…
Additional cooler as a
solution
For example, Chevrolet models often had the
following problem: engine operation temperatures in such models as AVEO or
CRUZE as well as in many other GM cars often reach approximately 115 degrees
(239°F). It turns out to be a real problem because these cars have a combined
cooler.

After 50-60 thousand kilometers (or even
earlier), the driver starts experiencing jolts and kicks. What is wrong? The
transmission simply gets overheated. This problem can be solved by installation
of an additional cooler. This component is mounted on the main radiator and
gives the car the following benefits:
- Elimination of overheating, usually the temperature does not exceed 80 degrees (176°F). It helps to prolong the transmission service life.
- Improved ATF cooling. Thus, ATF can be changed even after 60 thousand kilometers.
- Prolonged service life of the valve body and solenoids.
Pitfalls of additional cooler
In summer time, this system works
perfectly and causes no problems at all. The automatic transmission temperature
is unlikely to rise above 80-85 °C (176-185°F). But, what about winter time?
What is the outcome of increased automatic transmission cooling? ATF gets
thicker at low temperatures, therefore it is necessary to warm up the car
longer to prevent oil leakages from seals. It appears that this cooler is not
really needed in winter. So what’s to be done? Use the cooler in summer time
and remove it for the winter? No, just use a thermostat.
Thermostat
Additional coolers are very helpful for automatic transmissions, but they should be installed accurately. The thing is that the transmission should be cooled only at the right time (not constantly). Therefore, it is desirable to also install the thermostat when installing an additional cooler. This component opens the ATF supply only when it heats up to a certain temperature, say at 75 (167 °F). When there is no significant heating, ATF circulates on a small circle, i.e. operates in standard mode. When the oil heats up to 70-75 °C (158-167 °F) (sometimes up to 80 (176 °F), the thermostat opens a large circle through the installed external cooler, thus not allowing ATF to heat up to more than 70-85 degrees.
BMW E46 ATF thermostat removal and replacement
Application of the thermostat in
automatic transmission has the following advantages:
- Improved car warm-up in winter time;
- More efficient cooling in summer;
- Temperature control.
ATF change
It is recommended to change ATF in the automatic transmission on timely basis. This procedure is quite simple. Firstly, it is necessary to drive the car to a pit or car ramp and wait until the transmission oil cooling. Then it is necessary to unscrew a special bolt in the oil pan of the transmission case. Wait until the transmission fluid drains completely. Do not forget to disconnect hoses connected to the transmission cooling radiator and drain ATF from hoses and oil cooler. After that, screw the drain hole, add ATF in the gearbox to the maximum level and start the car. The car should operate for several minutes while the transmission oil reaches all transmission components, and then add more ATF to the required level. This operation can be performed independently or with the help of transmission specialists.
That’s how ATF can be changed independently
The automatic transmission cooling efficiency largely depends on the quality of used ATF. Therefore, it’s better to use original ATF products. Each car manufacturer recommends particular ATF options for their cars. Only usage of high-quality transmission fluids will help to ensure trouble-free operation of automatic transmissions.