Automatic transmissions have revolutionized the driving experience, providing seamless gear shifting and effortless maneuverability. But have you ever wondered how these marvels of engineering actually work? In this comprehensive article, we will take a deep dive into the inner workings of automatic transmissions, exploring their key components, the transmission process, and the role of transmission control systems.
Understanding the Basics
Automatic transmissions are complex systems designed to manage gear shifting without manual intervention. Unlike manual transmissions, which require the driver to engage gears using a clutch, automatic transmissions utilize a sophisticated arrangement of components and hydraulic systems to achieve smooth and precise gear changes.

Shift knob of Automatic on the left and Manual on the right
Key Components and Their Functions
Let's explore the essential components that make automatic transmissions function seamlessly:
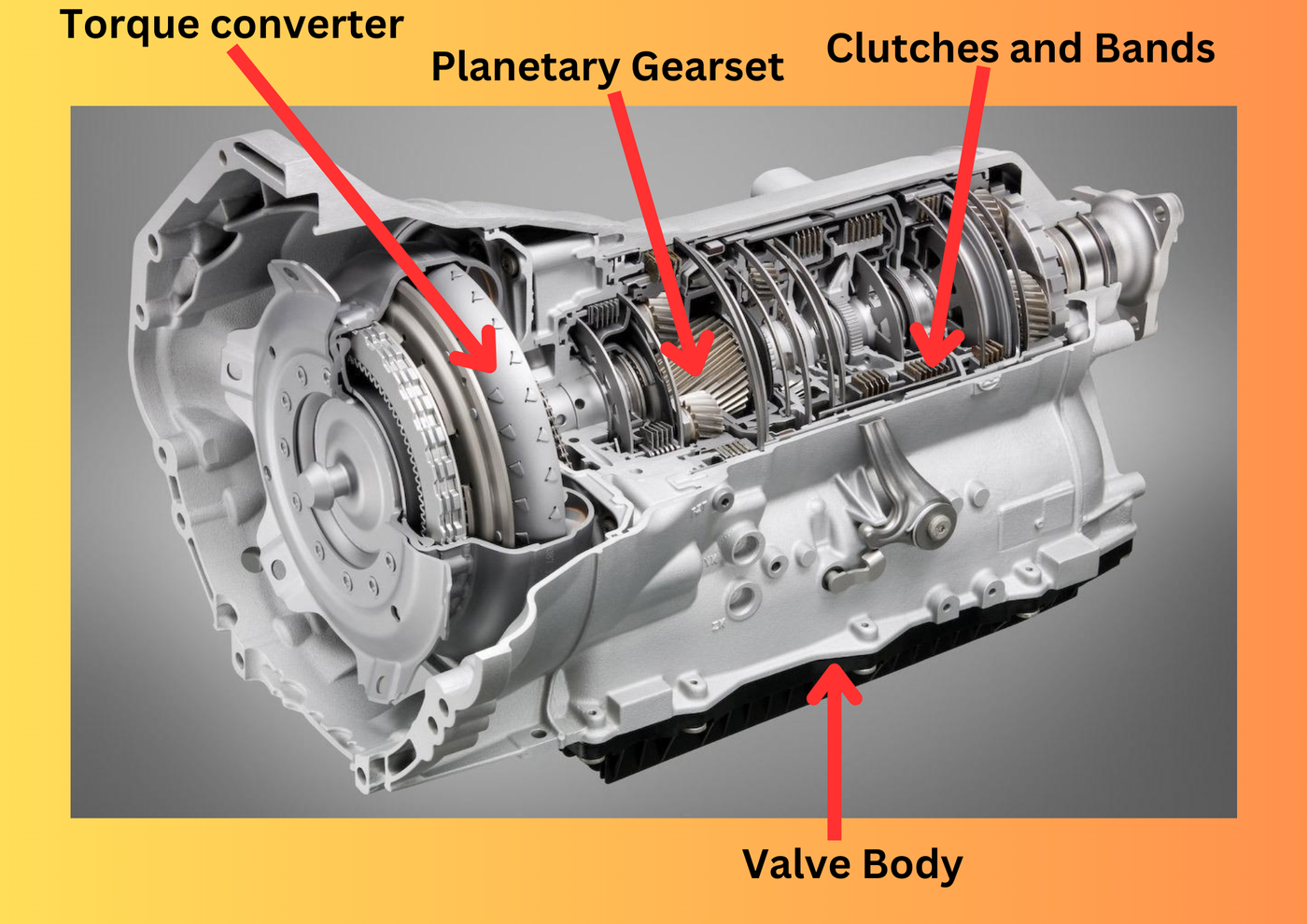
- Torque Converter: The torque converter serves as the connection between the engine and the transmission. It uses a fluid coupling to transmit torque from the engine to the transmission input shaft, allowing the engine to run even when the vehicle is stationary. The torque converter also provides torque multiplication, ensuring smooth power delivery.
- Planetary Gearset: The planetary gearset is a fundamental component of automatic transmissions. It consists of a sun gear, multiple planet gears, and a ring gear. By selectively engaging these gears, different gear ratios are achieved, allowing the vehicle to move at various speeds.
- Clutches and Bands: Clutches and bands play a crucial role in gear engagement and disengagement. They are controlled hydraulically and are responsible for connecting and disconnecting different sets of gears during gear changes.
- Valve Body: The valve body acts as the central control unit of the transmission. It contains a network of hydraulic control valves and solenoids that regulate fluid flow and pressure. By manipulating these valves and solenoids, the transmission can engage or disengage specific clutches and bands, facilitating precise gear changes.
The Transmission Process
Now, let's delve into the intricacies of the transmission process, which ensures smooth gear shifting and efficient power transfer:
- Idle and Gear Engagement: When the vehicle is started, the torque converter uses fluid coupling to transmit torque smoothly from the engine to the transmission. As the driver applies throttle and selects a gear, the appropriate clutches and bands engage to establish the desired gear ratio.
- Gear Shifting: During acceleration or deceleration, the transmission shifts gears to maintain optimal performance. The process involves the release and engagement of clutches and bands in a precise sequence. The valve body, through its control valves and solenoids, regulates fluid pressure and directs hydraulic systems to execute seamless gear shifts.
- Torque Converter Lock-up: To improve efficiency during highway cruising, modern automatic transmissions feature a torque converter lock-up mechanism. When engaged, the lock-up eliminates slippage in the torque converter, establishing a direct mechanical connection between the engine and the transmission. This reduces power loss and improves fuel efficiency.

Transmission Control Systems
To ensure the seamless operation of automatic transmissions, advanced transmission control systems are employed:
Electronic Control Units (ECUs): These sophisticated control units monitor inputs such as vehicle speed, throttle position, and engine load. They use this information to determine the optimal gear selection and timing for gear changes, ensuring smooth and efficient performance.

Transmission Control Module (TCM or TCU)
Sensors and Solenoids: Sensors located throughout the transmission provide crucial data to the ECUs, including transmission fluid temperature, speed sensor readings, and gear position. Solenoids, controlled by the ECUs, actuate hydraulic systems and engage or disengage clutches and bands to execute accurate gear shifts.
Valve Body: It acts as the central control center, orchestrating the intricate process of gear shifting and ensuring smooth and precise operation.
Comprised of a network of hydraulic control valves and solenoids, the valve body is responsible for regulating the engagement and disengagement of clutches and bands, which are crucial for gear changes. By manipulating these valves and solenoids, the transmission can select the appropriate gear ratio based on factors such as vehicle speed, throttle input, and driving conditions.
The valve body receives signals from sensors located throughout the transmission system, including speed sensors, temperature sensors, and throttle position sensors. These inputs provide essential information to the electronic control unit (ECU) that governs the transmission's operation. The ECU uses the data to make real-time decisions regarding gear selection and timing, sending signals to the valve body to actuate the necessary valves and solenoids.
When the driver selects a specific gear or accelerates, the valve body receives the corresponding signals and directs hydraulic pressure to the clutches and bands that need to engage or disengage. This process ensures a smooth and seamless transition between gears, allowing for efficient power transfer and optimum performance.
Additionally, the valve body controls other functions within the transmission, such as line pressure regulation, which ensures proper fluid pressure distribution to different components. It also manages the application of the torque converter lock-up mechanism, which eliminates slippage in the torque converter, improving fuel efficiency during highway driving.
Given its critical role in transmission operation, the valve body requires periodic maintenance and inspection to ensure optimal performance. Over time, debris and contaminants can accumulate within the valves and passages, affecting their functionality. Regular fluid changes and filter replacements are necessary to prevent clogs and maintain the integrity of the valve body.
In summary, the valve body is the control center of an automatic transmission, responsible for regulating fluid flow, pressure, and the engagement of clutches and bands. By precisely directing hydraulic pressure, the valve body enables smooth gear shifting and optimal performance. Its integration with the transmission control systems ensures seamless communication and coordination, resulting in a reliable and efficient driving experience.


Valve Body valves and simplified explanation on how they operate
By understanding the intricate mechanisms at work within automatic transmissions, you can appreciate the engineering prowess behind these remarkable systems. From the torque converter to the planetary gearset and the control systems, each component plays a vital role in delivering a smooth and efficient driving experience. Automatic transmissions continue to evolve, incorporating advanced technologies that enhance performance, fuel efficiency, and overall driving enjoyment.
While we have covered the basics of how automatic transmissions work in this article, it's important to acknowledge that the inner workings of these systems can be quite intricate and complex. Explaining every aspect of automatic transmission operation in simple terms can be challenging.
To provide a more comprehensive and visual understanding, we recommend watching a video that demonstrates the operation of an automatic transmission. Videos can effectively showcase the components, their movements, and the fluid dynamics involved in gear shifting. This visual representation can greatly enhance your comprehension of the concepts discussed in this article.
So, if you're eager to further explore the fascinating world of automatic transmissions, we encourage you to seek out and watch these valuable videos. They will provide you with a more in-depth understanding of the inner mechanisms, making it easier to grasp the complexities of this essential automotive technology.